Pmp Version 6 Chart
Looking at a career as a certified Project Management Professional (PMP)? This Cheat Sheet gives you quick, handy PMP certification facts to remember on test day to help you answer exam questions. You can review major project management concepts; key tools, techniques, outputs, and processes; and and some common equations found on the exam. Many key terms are defined in the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK) Guide Glossary.
Understand Scheduling Relationships for the PMP Certification Exam
When you’re ready to take the PMP (Project Management Professional) Certification exam, expect to see up to ten questions dealing with network diagrams, precedence diagramming, and scheduling issues. Here are some PMP details you need to know:
Dear Fahad, Thanks for sharing good and informative blogs, i have been regularly visiting your website and benefiting from your knowledge and information, recently, i did 100 Free PMP Exam Sample Questions and passed with percentage 90%, i just want to know here all the question is very easy such type of question can appear in real PMP exam, i will be appear for PMP exam in this month, i have. Alternatively, you can download a free pdf version of PMP process charts to study for the certification exam. The pdf file is 13 pages long and has the same content as the excel sheet but it lacks dynamic features of the excel sheet. If you begin your exam preparation now, the PMP® Exam will be based on PMBOK® Guide 5th edition by the PMP® Exam update. Summary: PMI updates the PMBOK® Guide and the PMP® Exam every several years as the practices of project management evolves. The new PMBOK® Guide edition (i.e. The 6th edition) has been published in the 3rd quarter of 2017.
FS = Finish-to-start
FF = Finish-to-finish
SS = Start-to-start
SF = Start-to-finish
Lead = The amount of time an activity can be advanced with respect to a predecessor activity
Lag = The amount of time a successor activity is required to be delayed with respect to a predecessor activity
A mandatory dependency is based on the nature of the work.
A discretionary dependency is based on a best practice or preferred way of doing something.
An external dependency is based on relationships outside the project.
An internal dependency is based on dependencies inside the project.
Pmp Edition 6 Process Chart
PMP Certification: 4 Estimating Techniques for Project Managers
You can apply PMP (project management professional) estimating techniques to resources, effort, duration, and costs. PMPs use different methods of estimating, depending on the situation.
Download anonymoX (Firefox) 3.0 for Windows. Browse the web anonymously on your Windows PC with anonymoX for the Firefox browser. AnonymoX is a free add-on for the Firefox browser which lets you stay anonymous while browsing thereby visiting blocked websites. Download the anonymoX now and hide your identity from malicious websites. AnonymoX is an initiative for anonymization in the internet. The aim is to restore the users right of anonymity in the web. Most websites monitor the behaviour. The anonymoX GmbH is a registered German company for anonymization on the internet. We provide a free add-on for Firefox and Google Chrome, as well as a Premium Service which will give you access to more and faster proxies. (With our tool you return the ability to bypass all sorts of Internet blockades.). AnonymoX on 32-bit and 64-bit PCs. This download is licensed as freeware for the Windows (32-bit and 64-bit) operating system on a laptop or desktop PC from firefox addons without restrictions. AnonymoX 4.3 is available to all software users as a free download for Windows 10 PCs but also without a hitch on Windows 7 and Windows 8. Free download anonymox mozilla firefox. Dec 13, 2018 Download anonymoX for Firefox. Easy anonymous web browsing. – Change your IP-Address and country – Visit blocked or censored websites. – Delete cookies, show your public ip, and more We provide the proxy servers, no external proxies or other programs required.
| Estimating method | Description |
|---|---|
| Analogous estimating | Generally used at the start of the project when not much is known. Compares the current project with past similar projects. A quick and relatively easy method of estimating, although not terribly accurate. |
| Parametric estimating | Used for estimates that are quantitatively based, such as dollars per square foot or number of installations per day. A relatively simple method, but not every activity or cost can be estimated quantitatively. |
| Three-point estimating | Accounts for uncertainty associated with estimating by determining an optimistic (best case, represented by O), most likely (represented by M), and pessimistic (worst case, represented by P) scenario. The most likely estimate is weighted most heavily. The equation is |
| Bottom-up estimating | Used when there is significant detail about the activity. A detailed assessment of the resources, capabilities, and amounts are used to determine an accurate duration or cost estimate. This is the most accurate method but also the most time-consuming and expensive form of estimating. |
- PMBOK 6 Knowledge Areas. 2 of the knowledge areas are renamed: Time management will be renamed to Schedule Management - this change will place an emphasis the importance of scheduling in project management.
- From PMP Certification All-in-One For Dummies, 2nd Edition. By Cynthia Snyder Stackpole. Looking at a career as a certified Project Management Professional (PMP)? This Cheat Sheet gives you quick, handy PMP certification facts to remember on test day to help you answer exam questions.
PMP Exam: Statistics for Normal and Cumulative Distributions
PMPs (project management professionals) often apply basic statistics to their projects. For the PMP certification exam, here’s what you need to know when dealing with normal and cumulative distributions:

Equations are based on a normal distribution. In a normal distribution, keep the following in mind:
68.3% of the data points fall within one standard deviation.
95.5% of the data points fall within two standard deviations.
99.7% of the data points fall within three standard deviations.
If you’re looking at a normal curve and need a cumulative distribution, you should remember these values:
0.15% of the data points fall between 0 and –3 from the mean.
2.25% of the data points fall between 0 and –2 from the mean.
16% of the data points fall between 0 and –1 from the mean.
84% of the data points fall between 0 and +1 from the mean.
97.75% of the data points fall between 0 and +2 from the mean
99.85% of the data points fall between 0 and +3 from the mean.
PMP Certification: 6 Strategies for Conflict Resolution
Experienced project management professionals (PMPs) know that as they plan and execute projects, they’ll encounter conflicts and differences of opinion. As you study for your PMP certification exam, become familiar with these six strategies to resolve conflict.
| Strategy | Description | Situation |
|---|---|---|
| Confronting / Problem-solving | Confronting the conflict as a problem to be solved | When you have confidence in the other party’s ability to problem solve When the relationship is important When you need a win-win solution |
| Collaborating | Win-win through collaboration and meeting to resolve issues | When there is time and trust When the objective is to learn When you want to incorporate multiple views When there is time to come to consensus |
| Compromising | When you are looking for some degree of satisfaction for both parties | When there is a willingness to give and take When both parties need to win When you can’t win When an equal relationship exists between the parties in conflict When the stakes are moderate To avoid a fight |
| Smoothing / Accommodating | Emphasize areas of agreement | To reach an overarching goal To maintain harmony When any solution will be adequate When you will lose anyway To create goodwill |
| Forcing | Win-lose; impose the resolution | When you are right In a do-or-die situation When the stakes are high To gain power If the relationship is not important When time is of the essence |
| Withdrawal / Avoiding | Retreat; cool off | When you can’t win When the stakes are low To preserve neutrality or reputation If the problem will go away on its own |
Pmp Version 6 Chart For Women
PMP Earned Value: Variances and Indexes
On the PMP certification exam, you’ll see five to ten questions on variances and indexes. Here’s fundamental information that project managers need to determine cost and schedule variances and indexes.
For variance and indexes, always start with EV.
When looking for information on schedule, use PV.
When looking for information on cost, use AC.
For a variance, subtract.
SV = EV – PV
CV = EV – AC
Negative is bad; positive is good.
For an index, divide.
SPI = EV / PV
CPI = EV / AC
Less than 1.0 is bad, greater than 1.0 is good.
8 Quality Control Tools to Know for PMP Certification
There are many ways to assess quality control, and professional project managers (PMPs) make good use of them. When you take the PMP certification exam, you should be able to apply the following quality control tools:
Natural reader voices download. You can bolster the synchronized information. Keeps eye strain from an excess of perusing. A one of a kind and multi-gadget supporting device.
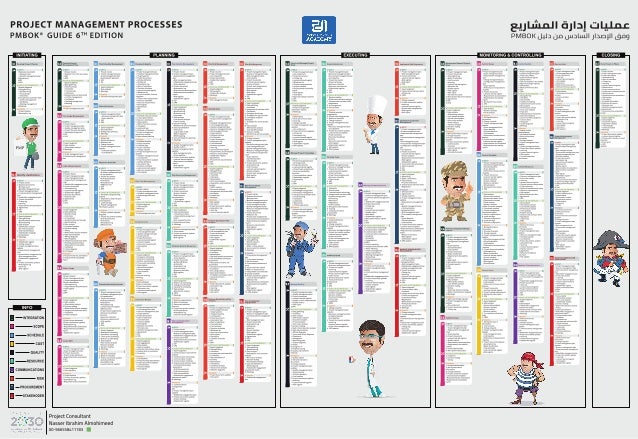
Pmp Version 6 Chart Template
Cause and effect diagram. Diagrams that define the inputs to a process or product in order to identify potential causes of defects.
Histogram. A bar chart showing a distribution of variables.
Run chart. Show trends in the variation of a process over time.
Scatter diagram. Shows the relationship between two variables.
Control chart. A graphic display of process data over time and against established control limits, and that has a centerline that assists in detecting a trend of plotted values toward either control limit.
Flowcharting. The depiction in a diagram format of the inputs, process actions, and outputs of one or more processes within a system.
Pareto chart. A histogram, ordered by frequency of occurrence, that shows how many results were generated by each identified cause.
Inspection. Examining or measuring to verify whether an activity or a component, product, result, or service conforms to specified requirements.